The calorific value of a fuel is the quantity of heat produced by its combustion – at constant pressure and under “normal” (standard) conditions (i.e. to 0oC and under a pressure of 1,013 mbar).
The combustion process generates water vapor and certain techniques may be used to recover the quantity of heat contained in this water vapor by condensing it.
- Higher Calorific Value (or Gross Calorific Value – GCV, or Higher Heating Value – HHV) – the water of combustion is entirely condensed and that the heat contained in the water vapor is recovered;
- Lower Calorific Value (or Net Calorific Value – NCV, or Lower Heating Value – LHV) – the products of combustion contains the water vapor and that the heat in the water vapor is not recovered.
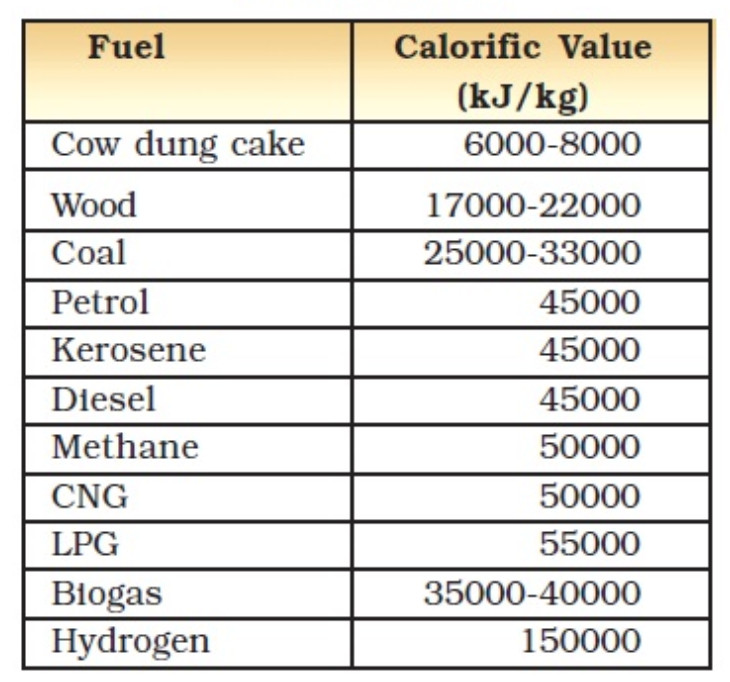
Fuel Calorific Values
| Natural gas | 12500 kcal/kg |
| Propane-butane | 11950 kcal/kg |
| Disel | 10000 kcal/kg |
| Fuel oil | 9520 kcal/kg |
| Brown coal | 3500 kcal/kg |
| Woods | 2500 kcal/kg |
| Electricity | 860 kcal/kWh |