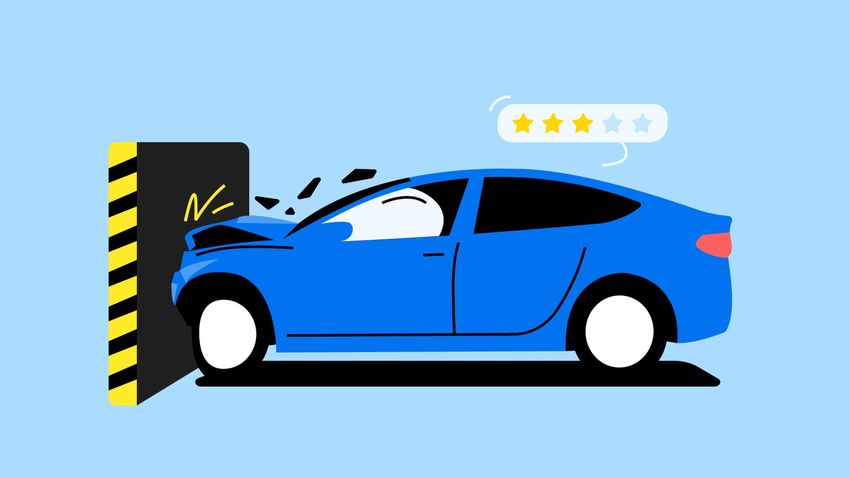
When you buy a car, safety is one of the most important factors to consider. But how do you know if a vehicle is actually safe? This is where crash tests come in.
Crash tests simulate real-world accidents to evaluate how well a vehicle protects its passengers. Organizations like NCAP (New Car Assessment Program), IIHS (Insurance Institute for Highway Safety), and Euro NCAP conduct these tests and assign safety ratings that help consumers make informed decisions.
Let’s dive into how crash tests work, what the ratings mean, and why they matter for your safety. 🚀🔍
🏆 The Purpose of Crash Tests
Crash tests analyze a car’s ability to protect passengers in various accident scenarios.
🔹 Key Goals of Crash Testing:
✔️ Measure how well a car absorbs impact energy
✔️ Evaluate the effectiveness of seat belts & airbags
✔️ Assess structural integrity (how well the car withstands crashes)
✔️ Improve vehicle design based on crash data
Car manufacturers use these tests to improve safety features, while consumers use them to compare vehicles before buying.
🔬 How Crash Tests Are Conducted
1️⃣ Preparing the Test 🚗📋
- A brand-new car is selected for testing.
- Crash test dummies (equipped with sensors) are placed inside.
- High-speed cameras and motion sensors are set up.
2️⃣ The Crash Test 💥
- The vehicle is accelerated toward an obstacle (barrier, pole, another vehicle).
- The crash happens at a controlled speed (typically 35-65 mph).
- Sensors on the dummies and vehicle record impact forces, airbag deployment, and structural deformation.
3️⃣ Data Collection & Analysis 📊
- Engineers analyze injury risk to the driver and passengers.
- The car’s structure, crumple zones, and restraint systems are evaluated.
- Based on the findings, the car receives a safety rating.
🚦 Types of Crash Tests
Different organizations conduct various crash tests to simulate real-world accident scenarios.
1️⃣ Frontal Crash Test 🔥
✅ Simulates a head-on collision, the most common type of car accident.
✅ The car crashes into a solid wall or deformable barrier at 35–40 mph.
✅ Measures driver & passenger injury risks.
🔹 Example: A car crashing into another vehicle at an intersection.
2️⃣ Side Impact Test 🚙💥🚗
✅ Simulates a T-bone collision where another car hits the vehicle from the side.
✅ Conducted using a moving barrier that strikes the test car’s side.
✅ Measures airbag effectiveness & door panel strength.
🔹 Example: A car being hit at a traffic light.
3️⃣ Rollover Test 🔄
✅ Simulates a car tipping over due to a sharp turn or side impact.
✅ Measures roof strength & seatbelt effectiveness.
✅ Determines how well passengers are protected in a rollover crash.
🔹 Example: A car flipping over in a high-speed curve.
4️⃣ Small Overlap Crash Test 🏎️💥
✅ Tests how a car handles a partial head-on collision (when only part of the front hits an object).
✅ Focuses on driver-side & passenger-side protection.
✅ More challenging because the impact is concentrated on a small area.
🔹 Example: A car hitting a pole or tree on one corner.
5️⃣ Pedestrian Impact Test 🚶💥🚗
✅ Evaluates how a car protects pedestrians in an accident.
✅ Measures head & leg injuries if a person is struck.
✅ Some cars have pedestrian airbags to reduce injuries.
🔹 Example: A pedestrian being hit at a crosswalk.
⭐ Understanding Car Safety Ratings
Different organizations assign safety ratings based on crash test results.
| Rating System | Region | Scoring System |
|---|---|---|
| NCAP (New Car Assessment Program) | Global | 5-star rating system ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| IIHS (Insurance Institute for Highway Safety) | USA | “Good” to “Poor” ratings |
| Euro NCAP | Europe | 5-star system with child & pedestrian protection scores |
How Ratings Work:
✔️ 5-Star Rating ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Excellent protection in crashes
✔️ 4 Stars ⭐⭐⭐⭐ = Good, but may lack advanced safety features
✔️ 3 Stars ⭐⭐⭐ = Average safety; may have weak areas
✔️ 2 Stars ⭐⭐ = Minimal protection; higher injury risk
✔️ 1 Star ⭐ = Poor protection; high fatality risk in severe crashes
🔧 Advanced Safety Features in Modern Cars
Car manufacturers use crash test data to develop better safety technologies.
🚗 Key Features That Improve Crash Safety:
✔️ Crumple Zones – Areas designed to absorb crash impact energy.
✔️ Airbags – Front, side, curtain, and knee airbags for protection.
✔️ Seatbelt Pretensioners – Tighten seatbelts in an accident.
✔️ Electronic Stability Control (ESC) – Prevents skidding & rollovers.
✔️ Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) – Detects obstacles & brakes automatically.
🚀 Real-World Impact: How Crash Tests Save Lives
🔹 Safer Vehicles = Fewer Fatalities
✔️ In the 1970s, over 50,000 people died annually in US car crashes.
✔️ Today, thanks to better crash protection, that number has dropped by half, despite more cars on the road.
🔹 Crash Tests Influence Car Design
✔️ Manufacturers improve airbags, crumple zones, and safety cages based on crash test results.
✔️ SUVs and trucks are now designed to be less deadly to smaller cars in collisions.
🔹 Better Consumer Awareness
✔️ Buyers can compare safety ratings before purchasing a car.
✔️ High crash-test scores increase consumer trust & sales.
🔮 The Future of Crash Testing
With advancements in AI and automation, crash testing is evolving:
🚗 Virtual Crash Simulations – AI-based models predict crash behavior without destroying physical cars.
🚗 Self-Driving Car Safety Tests – Evaluating how autonomous vehicles react in crash scenarios.
🚗 Smart Sensors & AI – Cars that detect and prevent accidents before they happen.
The ultimate goal? ZERO fatalities in car accidents. 🚀
🎯 Conclusion
Crash tests are essential for improving car safety and reducing road fatalities. By simulating real-world accidents, engineers can design stronger, safer vehicles that protect drivers, passengers, and pedestrians.
🚗 Next time you buy a car, check its crash test rating! It could be the difference between life and death.